https://www.zcyphygeodesy.com/en/h-nd-132.html
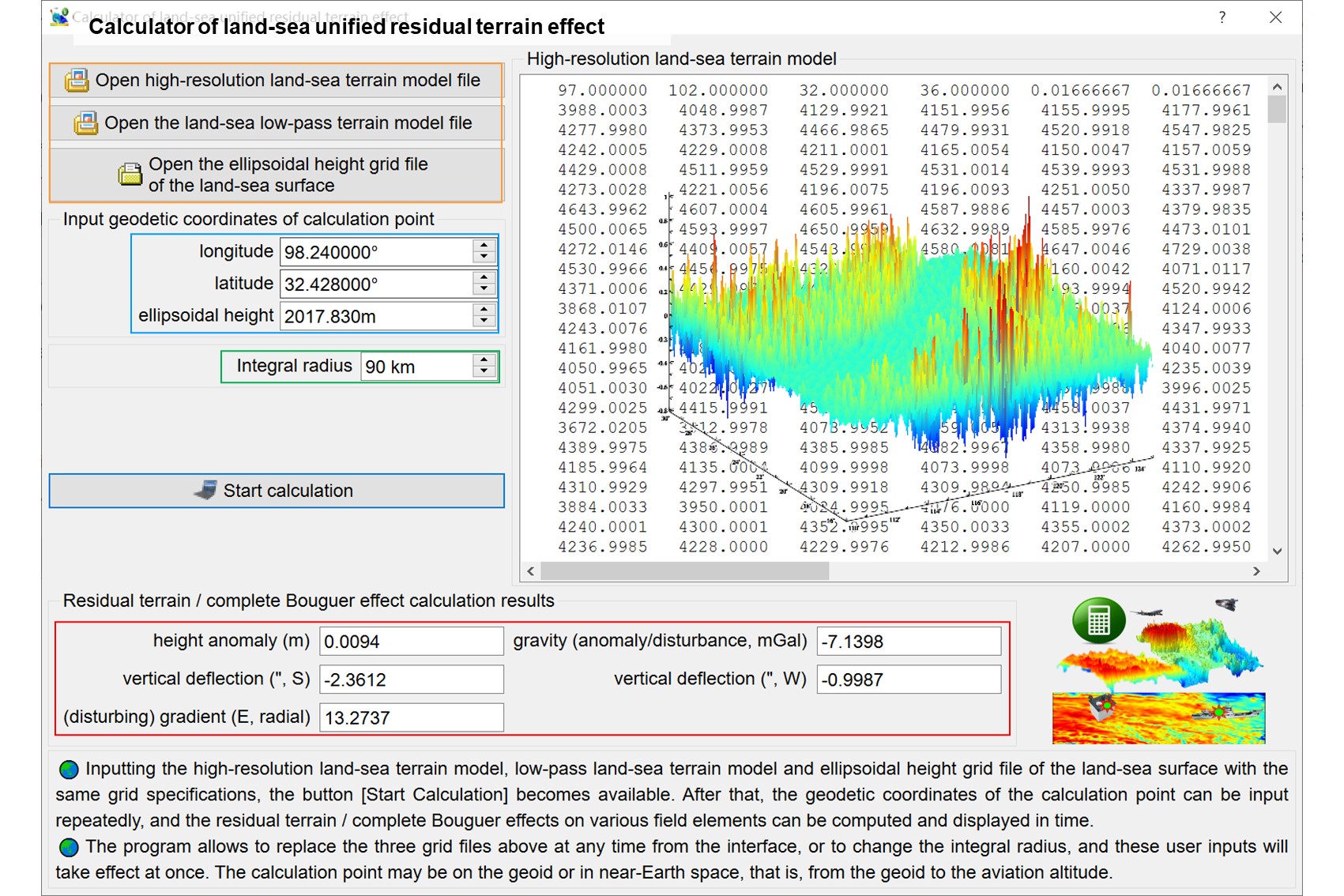
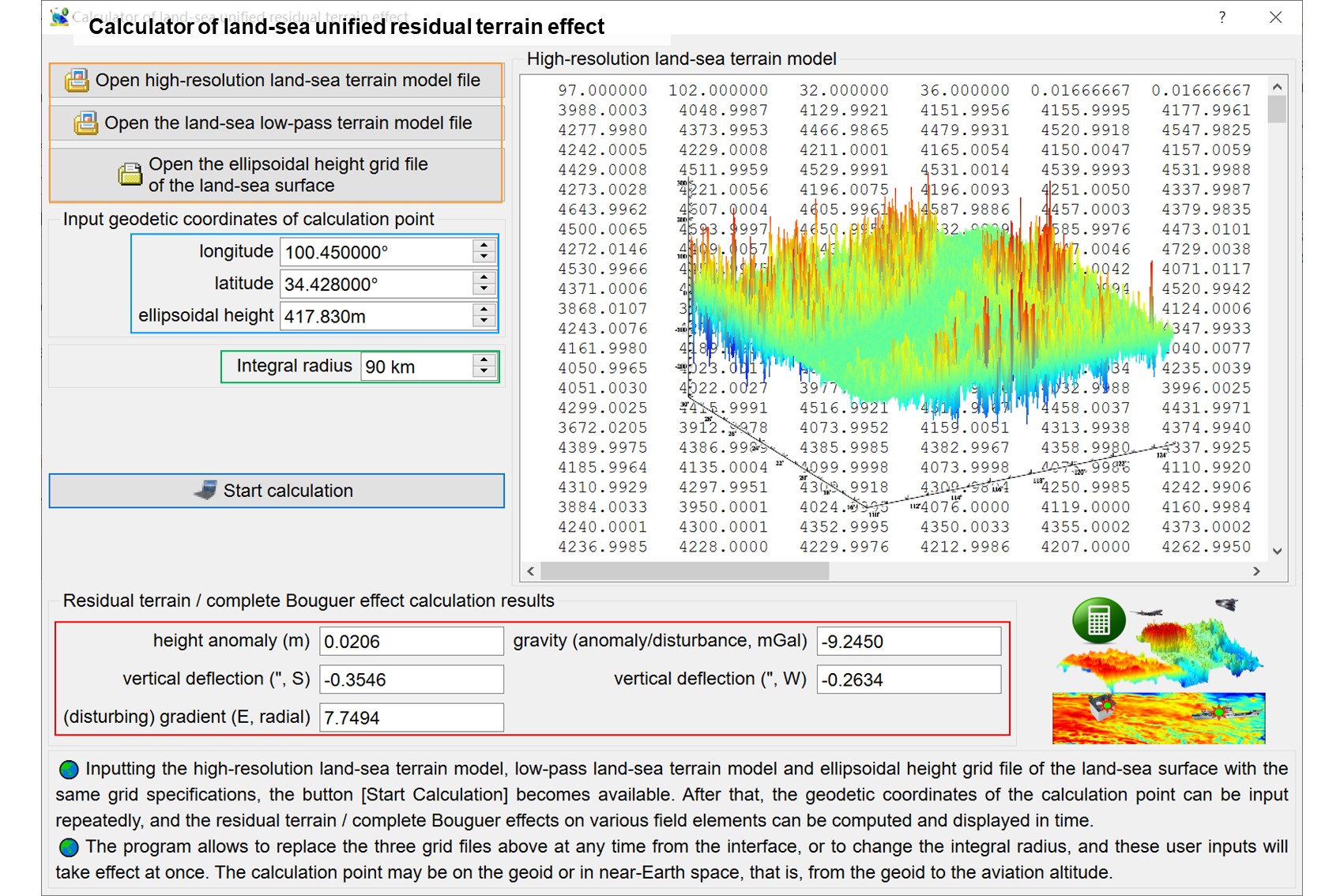
Using the rigorous numerical integral algorithm, from the high-resolution land-sea terrain model, low-pass land-sea terrain model and ellipsoidal height grid of the land-sea surface, compute the residual terrain effects on the height anomaly (m), gravity (anomaly/disturbance, mGal), vertical deflection (ʺ, to south, to west) or (disturbing) gravity gradient (E, radial) on or outside the geoid.
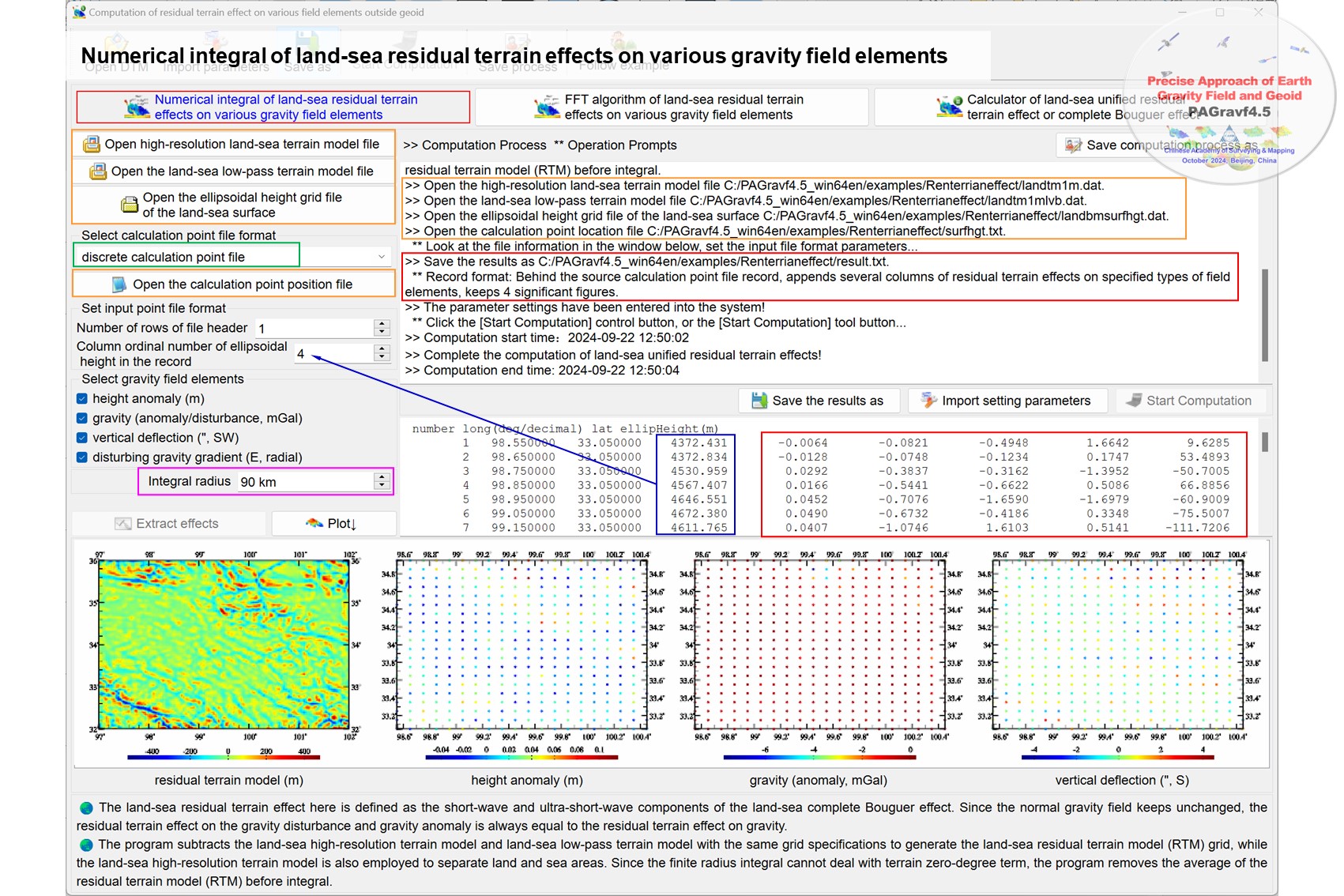
The land-sea residual terrain effect here is defined as the short-wave and ultra-short-wave components of the land-sea complete Bouguer effect. Since the normal gravity field keeps unchanged, the residual terrain effect on the gravity disturbance and gravity anomaly is always equal to the residual terrain effect on gravity.
The terrain effect on field element is equal to the negative value of the classic terrain correction, such as the local terrain effect is equal to the negative local terrain correction.
Compared with the local terrain effect and terrain Helmert condensation, the residual terrain effect is more conducive to modelling of geoid (height anomaly), suitable for processing of vertical deflection data such as for satellite altimetry data, but not conducive to processing of (disturbing) gravity gradient data.
RTMeffectnumintegral.f90
The record format of the input calculation point file: ID (point no / point name), longitude (decimal degrees), latitude (decimal degrees), ellipsoidal height (m)......
Input the high-resolution land-sea terrain model file, land-sea low-pass terrain model file and ellipsoidal height grid file of land-sea surface with the same grid specifications.
The record format of the output file reslt.txt: Behind the record of the calculation point file, appends 5 columns of land-sea residual terrain effects on the height anomaly (m), gravity (anomaly/disturbance, mGal), vertical deflection (ʺ, to south, to west) or (disturbing) gravity gradient (E, radial) on or outside the geoid.
It is recommended that the land-sea low-pass terrain model is constructed by the spherical harmonic synthesis from a global land-sea terrain mass spherical harmonic coefficient model to effectively improve the approach performance of gravity field.
RTMintegralBLH(BLH,dtm,sfh,rnt,nlat,nlon,hd,dr,GRS,ter)
Input parameters BLH(3) - longitude (decimal degrees), latitude (decimal degrees), ellipsoidal height (m) of the calculation point.
Input parameters: dtm(nlat,nlon) - the ground digital elevation model (normal /orthometric height) grid, which is employed to identify whether the moving integral area element is located on land or in the sea.
Input parameters: sfh(nlat,nlon) - the ground ellipsoidal height grid, which represents the terrian surface position employed to calculate the integral distance.
Input parameters: rnt(nlat,nlon) - the residual terrain model (RTM) grid.
Input parameters: dr, hd(6) - the integral radius (m) and grid specification parameters (minimum and maximum longitude, minimum and maximum latitude, longitude and latitude intervals of a cell grid).
Input parameters: GRS(6) - gm, ae, j2, omega, 1/f, default value
Return parameters: ter(5) - land-sea residual terrain effects (in unit of SI) on the height anomaly, gravity (anomaly/disturbance), vertical deflection (to south, to west) or (disturbing) gravity gradient (radial).
normdjn(GRS,djn); GNormalfd(BLH,NFD,GRS)
Return parameters: NFD(5) - the normal geopotential (m²/s²), normal gravity (mGal), normal gravity gradient (E), normal gravity line direction (', expressed by its north declination relative to the center of the Earth center of mass) or normal gravity gradient direction (', expressed by its north declination relative to the Earth center of mass).
LegPn_dt2(pn,dp1,dp2,n,t) ! t=cos ψ
BLH_RLAT(GRS, BLH, RLAT); BLH_XYZ(GRS, BLH, XYZ)
RLAT_BLH(GRS, RLAT, BLH)
CGrdPntD(lon,lat,dt,row,col,hd); CGrdPntD2(lon,lat,dt,row,col,hd)
CShepard(lon,lat,dt,row,col,hd); Gauss2D(lon,lat,dt,row,col,hd)
PickRecord(str0, kln, rec, nn); StatGrid(grid,row,col,rst)
Fortran90, 132 Columns fixed format. Fortran compiler for any operating system. No external link library required.
[Algorithmic formula] PAGravf4.5 User Reference https://www.zcyphygeodesy.com/en/
1.4.1 Format convention for geodetic data file
7.6.2 Integral algorithms of residual terrain effects on various field elements outside the geoid
7.1(4) Low-dgree Legendre function and its first and second derivative algorithms
The zip compression package includes the test project in visual studio 2017 - intel fortran integrated environment, DOS executable test file and all input and output data.