Chat with Joey is a TensorFlow implementation of A Neural Conversational Model (aka the Google chatbot) with the help of DeepQA repo. It make use of a seq2seq model RNN for sentence predictions. The chatbot is designed to mimic the personality of Joey, a character from the tv-show "F.R.I.E.N.D.S" (more about this under dataset).
Demo Video Link
To run the project you will need:
- python 3.5
- tensorflow (v0.12)
- django (1.10)
- channels
- Redis
- asgi_redis (at least 1.0)
- CKPT FILE
- Dataset
Once you have all the depenedencies ready, do the folowing:
Download the dataset friends.txt and move it to data/lightweight/.
Extract the ckpt zip file, you will get a folder 'model-server' with the ckpt file and its associated files. Move this folder to /save. The server will look at the model present on save/model-server/model.ckpt
To configure the web app
export CHATBOT_SECRET_KEY="my-secret-key"
cd chatbot_website/
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrateThen, to launch the server locally, use the following commands:
cd chatbot_website/
redis-server & # Launch Redis in background
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8888Go to the browser, if you are running it on a server then [ip-address]:8888, if you are on your local machine then localhost:8888
For this project we used the Friends TV Corpus, which was currated by David Ayliffe for his masters thesis to study inter-gender and intra-gender conversation. We formatted the data to get conversation between Joey(a character) and several other characters. There are two reasons for this:
-
We were targeting sentences with 5 words.
-
Joey has the highest number of conversations in the dataset.
Some of the hyperparameter we played with are sentence-length, number of hidden-layers, word embedding-size, batch-size and number of iterations. One thing to note here is that there is no logic behind these values, it was purely based on a trial and error approach.
-
We started training with sentences containing more than 20 words, It took more than 16 hours to train and still it was giving gibberish output. Then we reduced it to 10 words, although it was comparitively better we were not happy with the result. Finally we tried with 5 words and we got good outputs.
-
There are 2 RNN layers(encoder and decoder) and for each layer we put the number of hidden layers to 2048.
-
Changed the word embedding size to 256.
-
Batch size to 512.
-
Number of iteration to 200,000.
The model is a standard seq2seq RNN with two LSTM cells one for the encoder and another for the decoder, and 256 hidden units in each RNN cell. For the purpose of our project, we changed the number of hidden layers to 2048. Basically, tensorflow processes the data inside the encoder cell during training by applying three operations that compute the state of the cell. First is forget which determines what info to throw away from the previous cell state. For example, data that is not necessary to compute the current cell state. Second is input that determines what information is to let in from the new state. Finally, output that produces the final output from the cell. The encoder converts the input into vector representation and sends it to the decoder. Then the decoder is trained on both the output sequence as well as the input representation from the encoder. Since the model works on two sequences, it can predict new elements of a sequence given prior elements of the sequence. Deep Q&A model is trained on conversational corpus to predict sentences in response to users’ queries. There are different modules for the purpose of training the model and for the evaluation of the model. The main module is chabot that contains most of the sub-modules for training and testing functionalities. This module reads the user prompt and runs the training or testing mode and eventually returns a trained model for the training mode or starts a chatbot session for the testing mode. A brief explanation is provided below for the main modules.
- chatbot (module) Training mode: The training mode generates a graph for the model and starts a tensorflow session. The tensorflow session reads a batch of data and runs the training process to periodically minimize the loss function.
Testing mode: reads the user’s query and feeds the query to the encoder as a sequence of word ids. Then it runs the model with the batch of word ids to get a predicted sequence of word ids. The decoder then converts the predicted sequence into user readable string and returns it as an answer.
- Model (module) It contains the implementation of the model. It builds the model network and the computational graph with specified parameters. It basically creates two RNN cells using tensorflow, each of which with 2048 hidden layers. We increased the number of hidden layers from 256, and as mentioned above, it was purely based on a trial and error approach. There are also four defined tensorflow placeholders for the network inputs: encoder Inputs, decoder Inputs, decoder Targets same as decoder Inputs, and decoder Weights to adjust the learning to the target sentence size. The loss function is also defined using tensorflow seq2seq.sequence_loss call.
- Trainer (module) The Model module does not perform run on itself but just return the operators to do so. It’s actually the trainer module that launches the training with different parameters.
- Textdata (module) This module loads the dialogue corpus and builds the vocabulary. It also performs all the processing of the dataset. Some of these operations include extractConversation, extractText
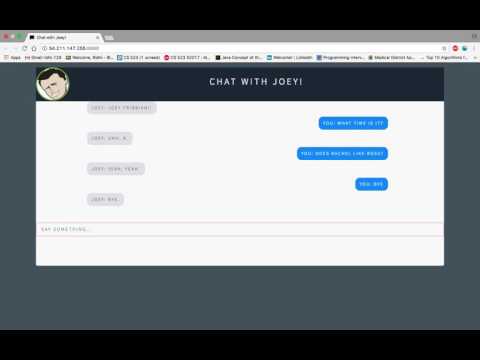
Below are some screenshots of our chat with the chatbot. It gives preety good results for standard questions as well as some character specific questions.
Good results
- The bot replies with the character name when asked : Who are you?
- Has a flirtatious nature just like Joey!
- Understands various greetings like Hi, Hello, Hey and responds accurately.
- Is smart enough to respond with a valid number when questioned: What time is it?
Random
It fails to respond appropriately to some questions. Q: What's up? A: Kidney Stones!
- Increase the sentence length from 5 to 10.
- Train multple characters from the show.
- Perform inter-bot chatting.
- Vinyals, Oriol, and Quoc Le. "A neural conversational model." arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.05869 (2015).
- Conchylicultor. "DeepQA." GitHub. N.p., Web. 27 Feb. 2017. https://github.com/Conchylicultor/DeepQA
- "Friends TV Corpus." David Ayliffe. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Feb. 2017. https://sites.google.com/site/friendstvcorpus/
- Mikolov, Tomas, et al. "Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality." Advances in neural information processing systems. 2013.
- Tensorflow. "Models." GitHub. N.p., Web. 22 Feb. 2017. https://github.com/tensorflow/models