-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Mathematical Operators
This section explains operators that perform mathematical operations on the items emitted by Observables.
-
count( )— counts the number of items emitted by an Observable and emits this count -
sum( )— adds the Integers emitted by an Observable and emits this sum -
sumLongs( )— adds the Longs emitted by an Observable and emits this sum -
sumFloats( )— adds the Floats emitted by an Observable and emits this sum -
sumDoubles( )— adds the Floats emitted by an Observable and emits this sum -
average( )— calculates the average of Integers emitted by an Observable and emits this average -
averageLongs( )— calculates the average of Longs emitted by an Observable and emits this average -
averageFloats( )— calculates the average of Floats emitted by an Observable and emits this average -
averageDoubles( )— calculates the average of Doubles emitted by an Observable and emits this average

The count( ) method returns an Observable that emits a single item: an Integer that represents the total number of items emitted by the source Observable, as shown in the following sample code:
def myObservable = Observable.create({ anObserver ->
anObserver.onNext('Three');
anObserver.onNext('Two');
anObserver.onNext('One');
anObserver.onCompleted();
});
myObservable.count().subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error encountered"); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);3
Sequence complete
- RxJS:
count - Linq:
Count - Introduction to Rx: Count
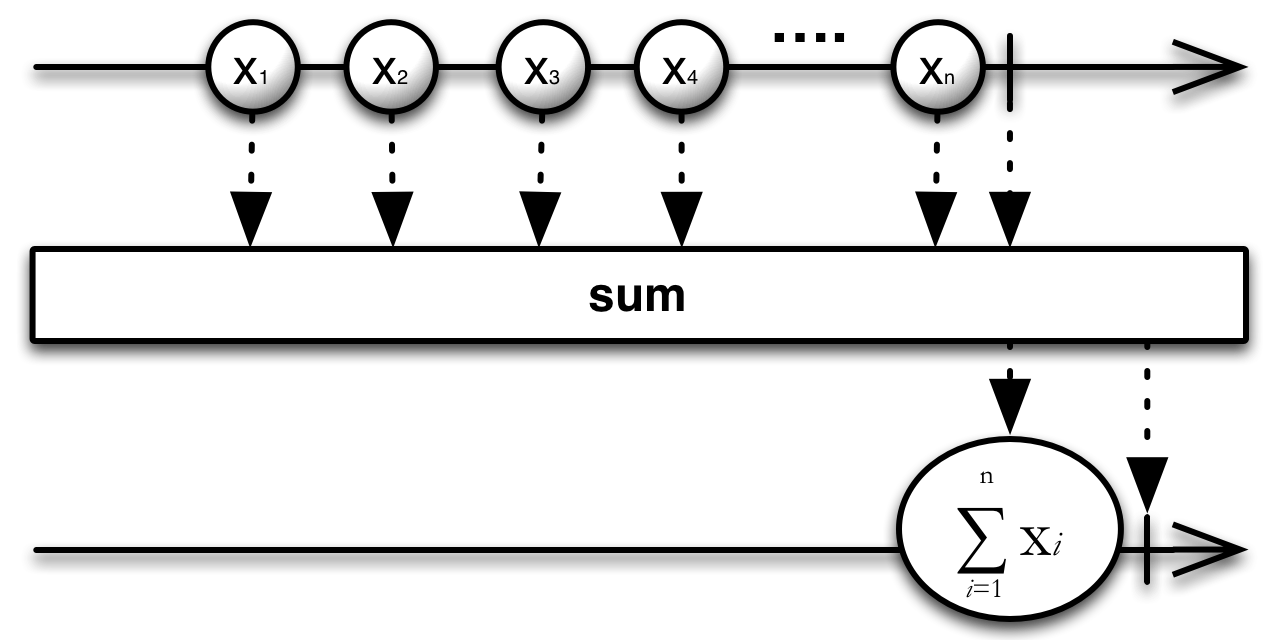
The sum( ) method returns an Observable that adds the Integers emitted by a source Observable and then emits this sum as an Integer, as shown in the following sample code:
def myObservable = Observable.create({ anObserver ->
anObserver.onNext(4);
anObserver.onNext(3);
anObserver.onNext(2);
anObserver.onNext(1);
anObserver.onCompleted();
});
myObservable.sum().subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error encountered"); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);10
Sequence complete
There are also specialized "sum" methods for Longs, Floats, and Doubles (sumLongs( ), sumFloats( ), and sumDoubles( )).
- RxJS:
sum - Linq:
Sum - Introduction to Rx: Min, Max, Sum, and Average

The average( ) method returns an Observable that calculates the average of the Integers emitted by a source Observable and then emits this average as an Integer, as shown in the following sample code:
def myObservable = Observable.create({ anObserver ->
anObserver.onNext(4);
anObserver.onNext(3);
anObserver.onNext(2);
anObserver.onNext(1);
anObserver.onCompleted();
});
myObservable.average().subscribe(
{ println(it); }, // onNext
{ println("Error encountered"); }, // onError
{ println("Sequence complete"); } // onCompleted
);2
Sequence complete
There are also specialized "average" methods for Longs, Floats, and Doubles (averageLongs( ), averageFloats( ), and averageDoubles( )).
A Netflix Original Production
Tech Blog | Twitter @NetflixOSS | Twitter @RxJava | Jobs