One of the most important operations in Computer Vision is Segmentation. Image segmentation is the task of clustering parts of an image together that belong to the same object class. This process is also called pixel-level classification. Here, it involves partitioning images (or video frames) into multiple complex segments or objects in order to produce optimum augmented images utilizing the U2Net and Rembg Image Proceesing Models with OpenVINO toolkit respectively.
The dawn of modern AI and machine learning has wholly altered the field of computer vision. Unlike classical computer vision, which relies more on complex coded mathematical functions and transforms, modern computer vision is primarily based on artificial intelligence’s deep learning techniques to perform computer vision tasks. Deep learning is a sub-branch of machine learning concerned with algorithms majorly inspired by the functionality of the human brain. The algorithm of a deep learning model is referred to as an artificial neural network.
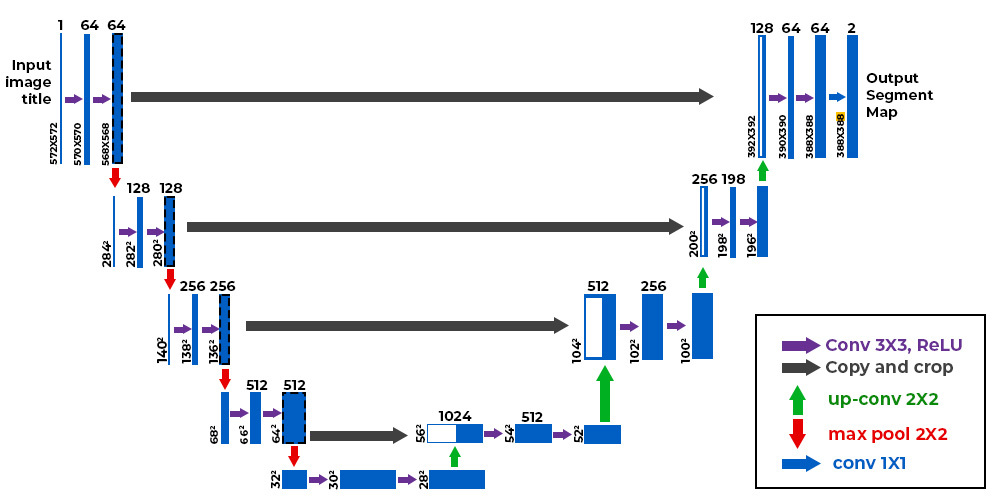
Figure: U-Net Architecture
The concept of convolutional neural networks in deep learning has majorly impacted how everyday computer vision tasks were thought of and approached. The artificial neural networks require a tremendous amount of input data for training purposes.
The convolutional neural networks take an image as an input and pass it through several convolutional and non-linear processes to output a so-called ‘‘feature map’ comprising the spatial information about the input image. The feature map is then used to extract an output label of the class, which is then compared with the known actual label of the input image class using a loss function.
This process is iteratively done for all the training examples present in the training data, and an optimized model is obtained. Then the optimized model is used to extract a label for a new image. The labels can be binary (0 and 1), or they can be more than two. The labels are binary when there are only two classes.
The concept behind semantic image segmentation is that each pixel of an image belongs to a particular class and is given that class’s label. The abstract idea about the method is that when each pixel is given a class label, the neural network is trained over numerous examples to learn what kind of pixel belongs to a particular class, let’s say foreground class, and which pixel belongs to the other class, the background one.
After the pixel classifier is trained, the resulting pixels with the label corresponding to the background class are assigned a shade of grey (usually white). The foreground image is retained as is; hence the background of the image is said to be removed.
The state-of-the-art methods used for the model building of semantic segmentation are ‘UNet’ and ‘DeepLab.’ Both architectures propose various techniques to acquire semantic segmentation, minimizing computational costs and maximizing accuracy.
1. Background Removal
2. Improve Resolution (Inference Engine)
3. Background Superimpose