-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 17
Credits Extension “CESER”
CESER - is the decentralized application working like a browser's extension connecting with the blockchain Credits. It allows you to connect directly to the network without entering a password on the sites increasing the security and usability. Create wallets and make transfers.
The goal of CESER (browser extension for Google Chrome & Opera) is to provide more secure and convenient user experience of websites based on Credits. In particular, it manages accounts and connects users to blockchain. Here are some CESER’s features:
• Allows users to manage their accounts and their keys with no context interaction of the site.
• Connects to nodes from different networks remotely. Fast synchronization with no need of waiting.
User registration using a private key
- Press the “CS Extension” button in a browser

The window will pop up

1. If you have a private key
Type your private key into the “Private Key” field and press the "Login" button.
2. If you don’t have your private key
Press “Create Key” button. The “key.json” file will be downloaded along with both public and private keys. Next, repeat the step from “1. If you have a private key” option.
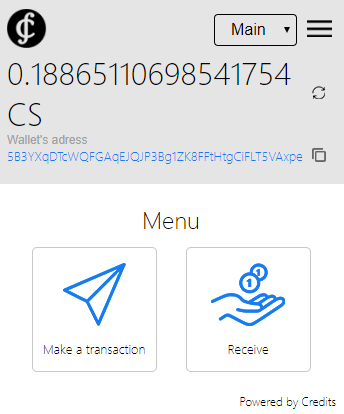
- Click the “Login” button. The following window will open:

In order to create a transaction, click the “Make a transaction” button. The window view:

-
Receiver’s address
-
Asset (choose a token type)
-
Amount (number of coins to be transferred)
- Press the “Send transaction” button. If all information was entered correctly, then the following window will be displayed asking to confirm a transaction.

- Confirm the transaction by pressing the “Confirm Transaction” button. It can be seen that the transaction was send successfully:

After pressing the “Receive” button
It will take you to

Here you can see account details. Also, information can be found through QRCode or the monitor page by clicking the “See on Monitor” button.
Download & Install
To start developing apps using CESER , you can download it here. The object “CreditsExtension” will appear in your console after installing the extension.
Run up a check on availability of the installed extension (example)
if(typeof CreditsExtension === "object")
{
//Code
}else{
// error processing
}
CreditsExtension.authorization(callBack)
• Checks user authorization in extension
• Awaits the callBack(response) function
• Object is going to be passed to response function:
{
message,
result
}
• If result is undefined, there will be a description of an error in message
• result is going to have a boolean value with a checking result.
CreditsExtension.authorization(r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
if(r.result)
{
alert(“user is authorized”)
}else{
alert(“user is not authorized”)
}
})
• Returns balance by a public key
• The object type will be passed to response variable (callBack)
{
message,
result:{
Credits_CS - CS user’s balance in a chosen network
}
}
• If result is undefined, there will be a description of an error in message
• result is going to have a boolean value with a checking result
• Obj looks like:
{
Key: public key whose data is requested
}
Can be undefined
If a key is not specified or Obj is undefined, then the balance of authorized wallet is going to be returned.
CreditsExtension.balanceGet(undefined,callBack)
CreditsExtension.balanceGet({},callBack)
CreditsExtension.balanceGet({Key:”Requested key”},callBack)
CreditsExtension.balanceGet({Key:”Requested key”},r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
// code
})
CreditsExtension.getHistory(Obj,callBack)
• Returns transaction history by a public key
• object Obj has a form of:
{
Page: page number,
Size: number of transactions per on page,
Key: public key whose transactions will be returned. If the key is not specified, transactions of an authorized user will be returned.
}
function callBack(response)
The objects will be passed to response as:
{
message,
result
}
• If result is undefined, there will be a description of an error in message
• result will contain an array from object type
{
id -transaction ID,
amount – amount transfer in CS,
fee – transaction fee (commission) in CS,
source – transaction sender’s public key
target - transaction receiver's public key
smartContract – smart contract information in a transaction
smartInfo – smart contract condition information
}
-
CreditsExtension.getHistory({Page:0,Size:100},callBack)
-
CreditsExtension.getHistory({Page:0,Size:100,Key:Public key},callBack)
CreditsExtension.getHistory({Page:0,Size:100}, r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
console.log(r.result);
});
Compiles a smart contract and reports compilation errors if those are found.
• line Code – smart contract code • function callBack(response) • The object will be passed to response as:
{
message,
result
}
• If result is undefined, there will be a description of an error in message
• result will contain an array from object type
{
name – class name,
byteCode – line with a byte code of a smart contract.
}
CreditsExtension.compiledSmartContractCode(“Code”, r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
console.log(r.result);
});
• Sends a transaction to blockchain;
• function callBack(response)
• The object will be passed to response as:
{
message,
result
}
If result is undefined, there will be a description of an error in message
To send a transaction for a CS transfer, the Transaction object must have the following form:
{
Target: Receiver’s public key ,
Amount: Amount Transfer,
Fee: Maximum transfer fee. If there is no value specified, an approximate amount of fee will be set in order
to complete the transaction.
}
CreditsExtension.sendTransaction({
Target: Public key,
Amount: “1.2”,
Fee: “0.1”
},r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
console.log(r.result);
});
To complete the smart contract method, the Transaction object must have the following form:
{
Target: Receiver’s public key ,
Fee: Maximum transfer fee. If not specified, then
SmartContract:
{
Params – parameters being passed to a method, array objects as:
{
K – data types (can be “STRING”, ”INT”, ”BOOL” ),
V – transmitted data
} The sequence of array corresponds to the sequence of arguments in the method.
Method – called method of a smart contract,
}
}
CreditsExtension.sendTransaction({
Target: Smart contract’s public key
Fee: “0.1”,
SmartContract:
{
Params: [
{K:“STRING”, V: “Test”},
{K:“INT”, V: 2},
{K:“BOOL”, V: true},
],
Method: “Test”
}
},r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
console.log(r.result);
});
In order to deploy smart contract, the Transaction object must have the following form:
{
Fee: Maximum transfer fee. If not specified, then
SmartContract:
{
Сode: Smart contract code
}
}
CreditsExtension.sendTransaction({
Fee: “0.9”,
SmartContract:
{
Сode: “Code”
}
},r => {
if(r.result === undefined){
alert(r.message);
return;
}
console.log(r.result);
});