I found a new intrest in learning algorithms and wanted to practice them and thought why not share them too! 🌘 Feel free to clone or reach out to me if you have any questions!✍🏼
- Sorting Algorithms: 🧮
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Searching Algorithms: 🔍
- Pattern Algorithms: 🧬
- Sliding window
- Two pointers
| Problems ❓ | Packages 🏮 |
|---|---|
| 1. Contiguous Sub-array | contiguousSubArray |
| 2. Maximum sum Sub-array | maxSumSubarray |
| 3. Smallest sum Sub-array | smallestSubarray |
| 4. Longest Substring with K Distinct Characters | |
| 5. Fruits into Basket | |
| 6. No-Repeat Sub-string | |
| 7. Permutation in a String 🏆 | |
| 8. 7. Anagram of a String 🏆 |
In many problems dealing with an array (or a LinkedList), we are asked to find or calculate something among all the contiguous subarrays (or sublists) of a given size. For example, take a look at this problem:
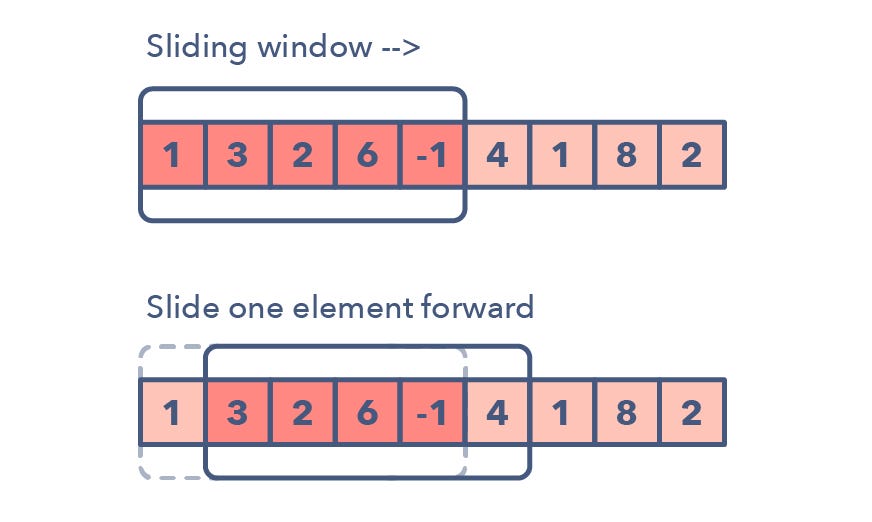
Given an array, find the average of all contiguous subarrays of size ‘K’ in it. Array: [1, 3, 2, 6, -1, 4, 1, 8, 2], K=5;
We are asked to find the average of all the elements in groups of 'K'. the output for the above example would be:
Output: [2.2, 2.8, 2.4, 3.6, 2.8]
✅ Solution:
- Using brute-force method,
- Using sliding window method.
This is the method where we calculate the average for each and every element one by one, therefore making the time complexity O(N*K) where N is the number of elements in the given array.
The efficient way to solve this problem would be to visualize each contiguous subarray as a sliding window of ‘5’ elements. This means that when we move on to the next subarray, we will slide the window by one element. So, to reuse the sum from the previous subarray, we will subtract the element going out of the window and add the element now being included in the sliding window. This will save us from going through the whole subarray to find the sum and, as a result, the algorithm complexity will reduce to O(N).
Here's a visual representation:
❓ Problem Statement:
Given an array of positive numbers and a positive number ‘k’, find the maximum sum of any contiguous subarray of size ‘k’.
Here are a few examples:
🗃️ Example 1:
Input: [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2], k=3 Output: 9 Explanation: Subarray with maximum sum is [5, 1, 3].
🗃️ Example 2:
Input: [2, 3, 4, 1, 5], k=2 Output: 7 Explanation: Subarray with maximum sum is [3, 4].
✅ Solution:
This problem can be solved using 2 methods.
- Brute-force method,
- window-sliding method.
I've solved it using both of the approaches.
The time complexity of the above algorithm will be O(N∗K), where ‘N’ is the total number of elements in the given array.
We take each element in groups of 'K' and calculate the sum. We then store the max value that is found with the max size being 'K'.
If you observe closely, you will realize that to calculate the sum of a contiguous sub-array we can utilize the sum of the previous sub-array. For this, consider each sub-array as a Sliding Window of size ‘k’. To calculate the sum of the next sub-array, we need to slide the window ahead by one element.
The time complexity is reduced to O(N).
❓ Problem Statement:
Given an array of positive numbers and a positive number ‘S’, find the length of the smallest contiguous sub-array whose sum is greater than or equal to ‘S’. Return 0, if no such sub-array exists.
✅ Solution:
Note that I have not taken care of the "Return 0, if no such subarray exists." because it's easy and I assume everyone is able to do it at this point.
This problem statement is fairly simply and can be easily tackled. There are once again, you guessed it, 2 ways to sole this problem.
- Brute-force method,
- sliding-window method.
Since I'm sure you will be comfortable with brute force at this point, I'll discontinue writing explanations for brute-force methods as they are pretty straight forward. I will explain special cases or if they are tough.
It's the same as the one before but this time it's just a tad bit different.
Since we are not given a size for the window, the size will keep changing. We start off with a windowEnd = 0 and then keep increasing the window size by adding elements one by one.
Here is a visual representation:
When the sum gets greater than 'S', we start reducing the window size by removing the leftmost element by using this code:
while (sum >= s){
if(windowLength < result) result = windowLength;
windowSum -= array[windowStart];
windowLength--;
windowStart++;
}❓ Problem Statement:
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring in it with no more than K distinct characters.
🗃️ Example 1:
Input: String="araaci", K=2 Output: 4 Explanation: The longest substring with no more than '2' distinct characters is "araa".
🗃️ Example 2:
Input: String="araaci", K=1 Output: 2 Explanation: The longest substring with no more than '1' distinct characters is "aa".
🗃️ Example 3:
Input: String="cbbebi", K=3 Output: 5 Explanation: The longest substrings with no more than '3' distinct characters are "cbbeb" & "bbebi".
✅ Solution:
In this question, we make use of a Hashmap. We traverse each character and add it to the hashmap to keep a count of it's frequency. The solution is pretty straight forward.. I've included comments to make you better understand the working of the code, so have a look at the code.
Java HashMap class implements the Map interface which allows us to store key and value pair, where keys should be unique. If you try to insert the duplicate key, it will replace the element of the corresponding key. It is easy to perform operations using the key index like updation, deletion, etc. HashMap class is found in the java.util package.
Syntax:
HashMap<Integer, Integer> myMap = new HashMap<>();Hashmap has many methods that can be used. The ones that I have used are:
| Method | Working |
|---|---|
| .put(Object key, Object value) | It is used to insert an entry in the map. |
| .get(Object key) | This method returns the object that contains the value associated with the key. |
| .getOrDefault(Object key, defaultValue) | It returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if the map contains no mapping for the key. |
You can use any data type in <key, value> but remember that you need to use data-type classes and not the primitive data types.
❓ Problem Statement:
Given an array of characters where each character represents a fruit tree, you are given two baskets and your goal is to put maximum number of fruits in each basket. The only restriction is that each basket can have only one type of fruit.
You can start with any tree, but once you have started you can’t skip a tree. You will pick one fruit from each tree until you cannot, i.e., you will stop when you have to pick from a third fruit type.
Write a function to return the maximum number of fruits in both the baskets.
🗃️ Example 1:
Input: Fruit=['A', 'B', 'C', 'A', 'C'] Output: 3 Explanation: We can put 2 'C' in one basket and one 'A' in the other from the subarray ['C', 'A', 'C']
🗃️ Example 2:
Input: Fruit=['A', 'B', 'C', 'B', 'B', 'C'] Output: 5 Explanation: We can put 3 'B' in one basket and two 'C' in the other basket. This can be done if we start with the second letter: ['B', 'C', 'B', 'B', 'C']
✅ Solution:
This question is pretty much similar to the longest sub-array. You can look into the code for further explanation.
❓ Problem Statement:
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring which has no repeating characters.
🗃️ Example 1:
Input: String="aabccbb" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest substring without any repeating characters is "abc".
🗃️ Example 2:
Input: String="abbbb" Output: 2 Explanation: The longest substring without any repeating characters is "ab".
🗃️ Example 3:
Input: String="abccde" Output: 3 Explanation: Longest substrings without any repeating characters are "abc" & "cde".
✅ Solution:
In this solution, we use the sliding-window approach. We use a hash-map to keep track of the highest index of the repeating character which will act as the starting point for the window.
At the same time, we will keep track of the longest length we have observed without any repetition of characters.
This is a challenge question 🏆
Level🎴 : Hard 🥇
I would highly encourage you to try this program out by yourself. If you haven't been doing so already, I would recommend actually trying to solve all the problems on your own before looking at the code thats provided. It'll definetly help you get better!
❓ Problem Statement:
Given a string and a pattern, find out if the string contains any permutation of the pattern.
❗Permutaion definition:
Permutation is defined as the re-arranging of the characters of the string. For example, “abc” has the following six permutations:
- abc
- acb
- bac
- bca
- cab
- cba
🗃️ Example 1:
Input: String="oidbcaf", Pattern="abc" Output: true Explanation: The string contains "bca" which is a permutation of the given pattern.
🗃️ Example 2:
Input: String="odicf", Pattern="dc" Output: false Explanation: No permutation of the pattern is present in the given string as a substring.
✅ Solution: The solution is pretty simple in our case. We can solve this problem using two methods:
- 💥 Brute-force Method,
- 🪟 Sliding-window Method.
In this method, we use two hash-maps to store the pattern and the part of a string. We then compare both the hashmaps and return true if they match.
This method is not really recommended because of the time-complexity issue and we end up using 2 hash-maps.
In this method, we store the charcters and their frequencies of the pattern in pattenrMap (hash-map).
We then traverse the string character by charcter and check if it is present in the hash-map.
If it is present, we reduce the frequency till it becomes 0, and we increment the matched variable.
If we end up not matching, then we decrease the window size and if the element being removed was part of the map, we add it back to the map by incrementing its frequency.
Further understanding can be done by checking the code.
This is a challenge question 🏆
Level🎴 : Hard 🥇
❓ Problem Statement:
Given a string and a pattern, find all anagrams of the pattern in the given string.
❗Anagram definition:
Anagram is actually a Permutation of a string. For example, “abc” has the following six anagrams:
- abc
- acb
- bac
- bca
- cab
- cba
🗃️ Example 1:
Input: String="ppqp", Pattern="pq" Output: [1, 2] Explanation: The two anagrams of the pattern in the given string are "pq" and "qp".
🗃️ Example 2:
Input: String="abbcabc", Pattern="abc" Output: [2, 3, 4] Explanation: The three anagrams of the pattern in the given string are "bca", "cab", and "abc".
✅ Solution:
The solution is the same as the previous challenge. The only difference is the output where you display the starting index of the anagram.
Try to solve this challenge out by yourself and then refer to the code pacakge if you get stuck.