Algorithm
-
Initiate
stackas an empty array. -
While
rootis not null:- To build an inorder traversal iteratively, go left as far as you can and add all nodes on the way into stack.
stack.append(root) root = root.left -
Pop the last element from stack
root = stack.pop(). -
Add the conditions and get
root.val -
Go one step right:
root = root.right.
Question : Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(root != null || !stack.empty()){
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return list;
}Question : Kth Smallest Element in a BST
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if(--k == 0) break;
root = root.right;
}
return root.val;
}# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
stack = list()
count = k
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if count == 1:
break
count -= 1
root = root.right
return root.valQuestion : Validate Binary Search Tree
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
# Iterative Inorder Traversal
stack = list()
node = -sys.maxsize-1
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if root.val <= node:
return False
node = root.val
root = root.right
return TrueQuestion : Inorder Successor in BST
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def inorderSuccessor(self, root: TreeNode, p: TreeNode) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
stack = list()
found = False
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if found:
return root
value = root.val
if value == p.val:
found = True
root = root.right
return rootQuestion : 270. Closest Binary Search Tree Value
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def closestValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], target: float) -> int:
if not root:
return None
difference = float("inf")
ans = 0
stack = list()
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if abs(root.val - target) < difference:
difference = abs(root.val - target)
ans = root.val
root = root.right
return ansQuestion: 783. Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
# Space Optimized Iterative Inorder Traversal
if not root:
return 0
child = None
stack = list()
ans = sys.maxsize
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if child:
ans = min(ans, root.val - child.val)
child = root
root = root.right
return ansQuestion: Binary Search Tree Iterator
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class BSTIterator:
def __init__(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]):
self.root = self.next = root
self.stack = list()
def next(self) -> int:
node = self.curr
while node:
self.stack.append(node)
node = node.left
node = self.stack.pop()
self.next = node.right
return node.val
def hasNext(self) -> bool:
if self.next or self.stack:
return True
return False
# Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = BSTIterator(root)
# param_1 = obj.next()
# param_2 = obj.hasNext()Question : Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
"""
class Solution:
def treeToDoublyList(self, root: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
if not root:
return root
stack = list()
linked_list = list()
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
linked_list.append(root)
root = root.right
node = linked_list[0]
self.head = node
for next_node in linked_list[1:]:
node.right = next_node
next_node.left = node
node = next_node
node.right = self.head
self.head.left = node
return self.headQuestion: Minimum Absolute Difference in BST
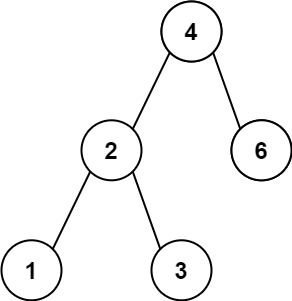
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), return the minimum absolute difference between the values of any two different nodes in the tree.
Input: root = [4,2,6,1,3]
Output: 1
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
stack = list()
left_child_found = False
ans = float('inf')
while stack or root:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
root = stack.pop()
if left_child_found:
ans = min(ans, abs(root.val - child))
left_child_found = True
child = root.val
root = root.right
return ansQuestion: Two Sum BSTs
Given the roots of two binary search trees, root1 and root2, return true if and only if there is a node in the first tree and a node in the second tree whose values sum up to a given integer target.
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3], target = 5
Output: true
Explanation: 2 and 3 sum up to 5.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def twoSumBSTs(self, root1: Optional[TreeNode], root2: Optional[TreeNode], target: int) -> bool:
stack1, stack2 = list(), list()
memo = collections.defaultdict(int)
while stack1 or root1:
while root1:
stack1.append(root1)
root1 = root1.left
root1 = stack1.pop()
if not root1.val in memo:
memo[target - root1.val] = root1.val
root1 = root1.right
while stack2 or root2:
while root2:
stack2.append(root2)
root2 = root2.left
root2 = stack2.pop()
if root2.val in memo:
return True
root2 = root2.right
return False