- 标签:深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、并查集、图
- 难度:中等
描述:一个 n 个节点的树(节点值为 1~n)添加一条边后就形成了图,添加的这条边不属于树中已经存在的边。图的信息记录存储与长度为 n 的二维数组 edges,edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中在 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。
现在给定代表边信息的二维数组 edges。
要求:找到一条可以山区的边,使得删除后的剩余部分是一个有着 n 个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回数组 edges 中最后出现的边。
说明:
-
$n == edges.length$ 。 -
$3 \le n \le 1000$ 。 -
$edges[i].length == 2$ 。 -
$1 \le ai < bi \le edges.length$ 。 -
$ai ≠ bi$ 。 -
$edges$ 中无重复元素。 - 给定的图是连通的。
示例:
- 示例 1:
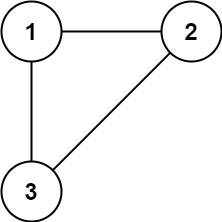
输入: edges = [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
输出: [2,3]- 示例 2:
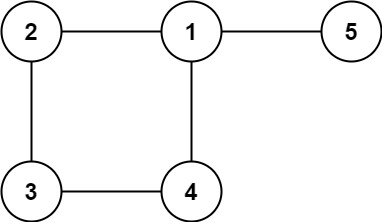
输入: edges = [[1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [1,4], [1,5]]
输出: [1,4]树可以看做是无环的图,这道题就是要找出那条添加边之后成环的边。可以考虑用并查集来做。
- 从前向后遍历每一条边。
- 如果边的两个节点不在同一个集合,就加入到一个集合(链接到同一个根节点)。
- 如果边的节点已经出现在同一个集合里,说明边的两个节点已经连在一起了,再加入这条边一定会出现环,则这条边就是所求答案。
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = [i for i in range(n)]
def find(self, x):
while x != self.parent[x]:
self.parent[x] = self.parent[self.parent[x]]
x = self.parent[x]
return x
def union(self, x, y):
root_x = self.find(x)
root_y = self.find(y)
self.parent[root_x] = root_y
def is_connected(self, x, y):
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
class Solution:
def findRedundantConnection(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
size = len(edges)
union_find = UnionFind(size + 1)
for edge in edges:
if union_find.is_connected(edge[0], edge[1]):
return edge
union_find.union(edge[0], edge[1])
return None-
时间复杂度:$O(n \times \alpha(n))$。其中
$n$ 是图中的节点个数,$\alpha$ 是反Ackerman函数。 - 空间复杂度:$O(n)$。