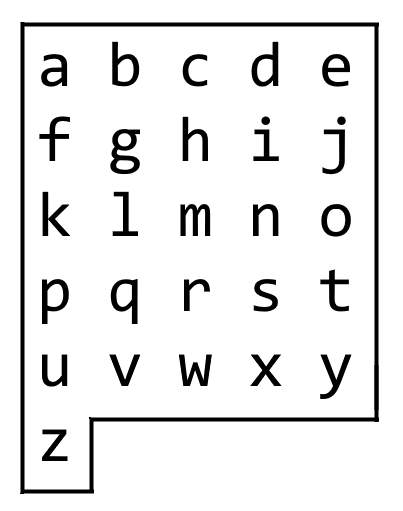
On an alphabet board, we start at position (0, 0), corresponding to character board[0][0].
Here, board = ["abcde", "fghij", "klmno", "pqrst", "uvwxy", "z"], as shown in the diagram below.
We may make the following moves:
<li><code>'U'</code> moves our position up one row, if the position exists on the board;</li>
<li><code>'D'</code> moves our position down one row, if the position exists on the board;</li>
<li><code>'L'</code> moves our position left one column, if the position exists on the board;</li>
<li><code>'R'</code> moves our position right one column, if the position exists on the board;</li>
<li><code>'!'</code> adds the character <code>board[r][c]</code> at our current position <code>(r, c)</code> to the answer.</li>
(Here, the only positions that exist on the board are positions with letters on them.)
Return a sequence of moves that makes our answer equal to target in the minimum number of moves. You may return any path that does so.
Example 1:
Input: target = "leet" Output: "DDR!UURRR!!DDD!"
Example 2:
Input: target = "code" Output: "RR!DDRR!UUL!R!"
Constraints:
<li><code>1 <= target.length <= 100</code></li>
<li><code>target</code> consists only of English lowercase letters.</li>