在Android开发中,矩阵是一个非常强大且有趣的工具,在之前的一篇文章中对ColorMatrix的原理进行了详细的分析,用其实现了一些简单的颜色过滤功能,这一次我们来探寻一下同样强大的Matrix,它具有更改图像图形的有趣功能。我们先来看看Matrix的结构。
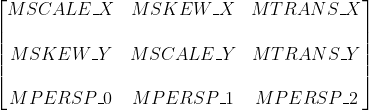
我们可以看到Matrix是一个3X3的矩阵。
- MSCALE_X、MSCALE_Y、MPERSP_2 分别表示X、Y、w(透视)的缩放
- MSKEW_X、MSKEW_Y 分别表示X、Y的错切
- MTRANS_X、MTRANS_Y 分别表示X、Y的平移
- MPERSP_0、MPERSP_1 分别表示X、Y方向上的透视
在Android的很多地方其实都使用到了Matrix的方法,比如图片、Canvas、动画等,我们这里以图片为例,像在Canvas与ValueAnimator章节中一样,在onDraw函数中我们先绘制一个坐标系,然后来绘制一个矩形。
// 平移画布
canvas.translate(mWidth/2,mHeight/2);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(1);// 恢复画笔默认宽度
// 绘制X轴
canvas.drawLine(-mWidth/2*0.8f,0,mWidth/2*0.8f,0,mPaint);
// 绘制Y轴
canvas.drawLine(0,-mHeight/2*0.8f,0,mHeight/2*0.8f,mPaint);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
// 绘制X轴箭头
canvas.drawLines(new float[]{
mWidth/2*0.8f,0,mWidth/2*0.8f*0.95f,-mWidth/2*0.8f*0.05f,
mWidth/2*0.8f,0,mWidth/2*0.8f*0.95f,mWidth/2*0.8f*0.05f
},mPaint);
// 绘制Y轴箭头
canvas.drawLines(new float[]{
0,mHeight/2*0.8f,mWidth/2*0.8f*0.05f,mHeight/2*0.8f-mWidth/2*0.8f*0.05f,
0,mHeight/2*0.8f,-mWidth/2*0.8f*0.05f,mHeight/2*0.8f-mWidth/2*0.8f*0.05f,
},mPaint);
// 创建矩阵
mMatrix = new Matrix();
/**
* 测试的Matrix操作
*/
// 绘制图片
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap,mMatrix,null);将点的X轴和y轴方向分别缩放和倍。x、y的计算结果为 :


用矩阵表示 :

现在我们使用Matrix自带的setScale方法 :
/**
* 测试的Matrix操作
*/
mMatrix.setScale(0.5f,0.5f);
Log.d("TAG",mMatrix.toString());
// Log
D/TAG: Matrix{[0.5, 0.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.5, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0]}错切变换的效果就是让所有点的x坐标(或者y坐标)保持不变,而对于的y坐标(或者x坐标)则按照比例发生平移。
保持y不变,但其x坐标则按比例发生平移。x、y的计算结果为 :


用矩阵表示 :

保持x不变,但其y坐标则按比例发生平移。x、y的计算结果为 :


用矩阵表示 :

当然你也可以同时进行水平错切和垂直错切的变换。
现在我们使用Matrix自带的setSkew方法 :
/**
* 测试的Matrix操作
*/
mMatrix.setSkew(0f,0.5f);
Log.d("TAG",mMatrix.toString());
// Log
D/TAG: Matrix{[1.0, 0.0, 0.0][0.5, 1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0]}假设有坐标为[](http://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?$$ x_0、y_0 $$),将其点进行平移,移动到点[](http://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?$$ x、y $$),其x、y计算结果为 :


用矩阵表示 :

现在我们使用Matrix自带的setTranslate方法 :
/**
* 测试的Matrix操作
*/
mMatrix.setTranslate(-200,-200);
Log.d("TAG",mMatrix.toString());
// Log
D/TAG: Matrix{[1.0, 0.0, -200.0][0.0, 1.0, -200.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0]}假设有一点坐标为[](http://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?$$ x_0、y_0 $$),距离原点为r,与x轴方向的夹角为α,绕原点旋转θ后,变换为点[](http://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?$$ x、y $$),其变换前后各点计算结果为 :



= r \cdot\cos\alpha\cos\theta - r \cdot\sin\alpha\sin\theta
= x_0\cos\theta - y_0\sin\theta
$$)

= r \cdot\sin\alpha\cos\theta + r \cdot\cos\alpha\sin\theta
= y_0\cos\theta + x_0\sin\theta
$$)
用矩阵表示为 :

现在我们使用Matrix自带的setRotate方法 :
/**
* 测试的Matrix操作
*/
mMatrix.setRotate(180);
Log.d("TAG",mMatrix.toString());
// Log
D/TAG: Matrix{[-1.0, -0.0, 0.0][0.0, -1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0]}我们在之前的变换中,一直没有说到最后一行的三个参数MPERSP_0、MPERSP_1、MPERSP_2,这里我们来稍微聊聊这三个参数所表示的透视。我们一般在图像中的一个点将使用如下方式进行表示(x, y, w),而Android中的二维矩阵计算是基于齐次坐标的,齐次坐标要求w的值为1,所以这个点的表示方法就变化为(x/w, y/w, 1)。
透视变换的效果其实类似于投影机的方式,我们看下w=3时,坐标(15,21,3)的效果 :

现在看下(15,21,3)计算出的齐次坐标系坐标(5,7,1)的效果 :
根据这个规则,也就解释了我们在使用过程中修改MPERSP_2参数时,图像会发生的类似缩放的效果,其实就是透视变换的效果。
现在我们使用Matrix自带的setValues方法 :
/**
* 测试的Matrix操作
*/
mMatrix.setValues(new float[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1.5f});
Log.d("TAG",mMatrix.toString());
// Log
D/TAG: Matrix{[1.0, 0.0, 0.0][0.0, 1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.5]}Matrix前乘与后乘的情况跟我在之前的文章ColorMatrix详解中ColorMatrix相乘章节所描述的基本相同。
前乘相当于,当前矩阵乘以输入的矩阵
示例如下:
mMatrix.reset();
mMatrix.preScale(sx,sy);
mMatrix.preTranslate(tx,ty);用矩阵表示为 :

后乘相当于,输入的矩阵乘以当前矩阵
mMatrix.reset();
mMatrix.postScale(sx,sy);
mMatrix.postTranslate(tx,ty);
本文深入分析了Matrix的原理,并讲解了其常用方法和前后乘的方法。如果在阅读过程中,有任何疑问与问题,欢迎与我联系。
博客:www.idtkm.com
GitHub:https://github.com/Idtk
微博:http://weibo.com/Idtk
邮箱:IdtkMa@gmail.com
Matrix
Android Matrix
Android中关于矩阵(Matrix)前乘后乘的一些认识
齐次坐标系入门级思考
次坐标和投影
变换矩阵












